Cell type-specific and disease-associated eQTL in the human lung
Posted on
表达数量性状位点(expression quantitative trait locus, eQTL)是一类能够影响基因表达量的遗传位点(大部分都是单核苷酸多态性,SNP)
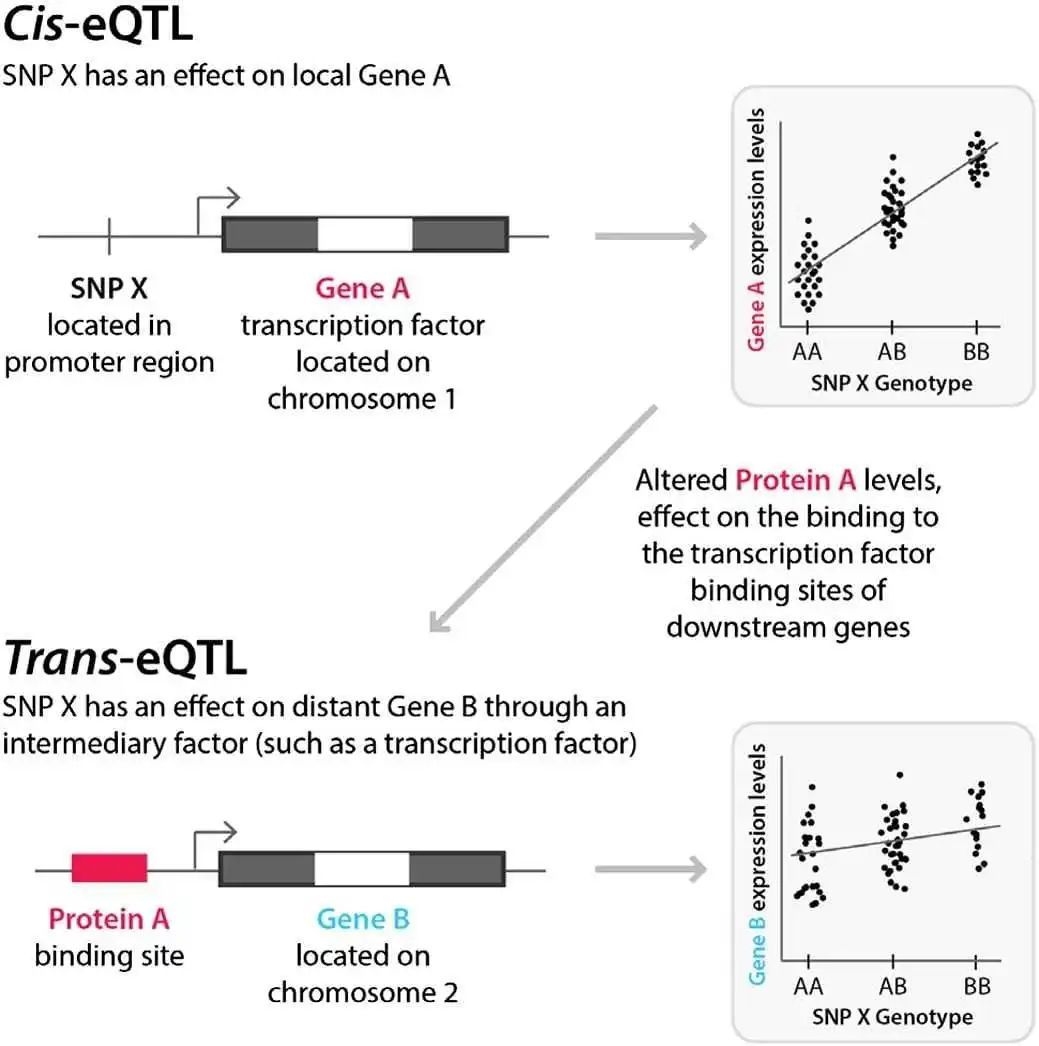
一般而言,eQTL主要分为两类:(1)顺式eQTL(cis-eQTL):它主要是指与所调控基因相距较近的eQTL,一般多位于所调控基因的上下游1Mb区域;(2)反式eQTL(trans-eQTL):与cis-eQTL恰恰相反,反式是指距离所调控基因位置比较远的eQTL,有时候距离甚至超过5Mb。因此,对于eQTL分析而言,我们通常需要考虑两点,SNP和基因表达水平的关联度以及SNP与基因的距离。
利用原始数据做eQTL分析,我们至少需要三个文件,第一个是样本信息文件,该文件包含样本的年龄,性别和人种等等;第二个是基因表达量文件,它表示的是每个基因在每个样本中的表达含量;第三个是基因型数据,也即每个样本的基因型数据。
gene1 ~ snp1 + sex + age + error_term
source: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/378403055
表达数量位置的基因座,它指的是染色体上一些能特定调控mRNA和蛋白表达水平的区域,其mRNA/蛋白质的表达水平量与数量性状成比例关系。eQTL analysis是将基因表达水平的变化和基因型连接起来,研究遗传突变与基因表达的相关性。
source: https://xsliulab.github.io/Workshop/2021/week32/eqtl%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E6%96%B9%E6%B3%95.html
Background: sc-eQTL studies
Motivation of eQTL studies: many disease-associated variants identified in GWAS are located in the regulatory regions of the genome and contribute to disease risk and progression by effecting changes in gene expression.
- Bulk RNA-seq -> single cell RNA-seq
- Tissue-specific -> cell-type-specific or context-dependent
Background: IPF
GWAS and meta-analyses have identified many IPF-associated variants, some of these variants are eQTLs in bulk-lung tissue; however, their cell-type-specific regulatory consequences have not been explored.
Methods
- Pseudo-bulk mean aggregation.
- Perform single-cell-level normalization using scran, and then calculate the mean on the resulting normalized (logged) counts.
- Perform eQTL mapping with a linear mixed model (LMM).
- The random effect term in LMM accounts for the expected correlation between cells from the same donor as well as genetic relatedness between donors, e.g. the kinship matrix.
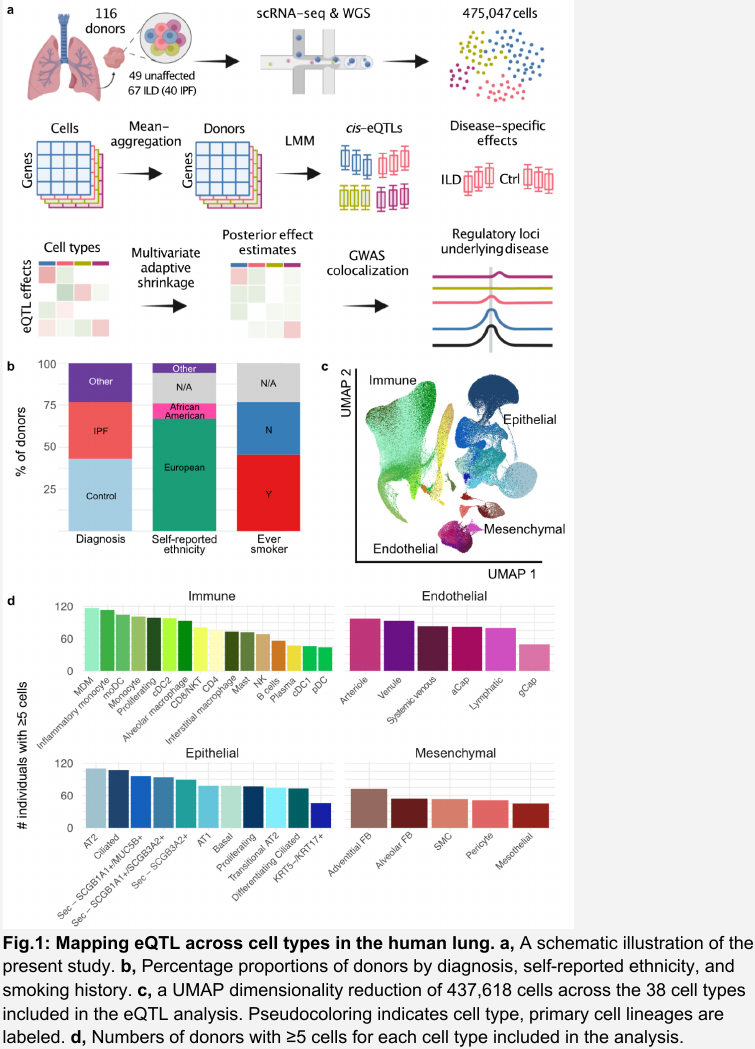
- A gene was considered as eGene for a cell type if any eQTL for that gene was significant.



int-eQTL: disease-state interaction eQTL